Formulae & Assumptions
Dilute Binary Liquid Solutions
The thermal conductivity of liquids is calculated
using Bridgman’s equation (BSL Eqn 9.4-3).
This equation is limited to densities well above the critical density
because of the assumption that each molecule oscillates in a “cage” formed by
its nearest neighbors.
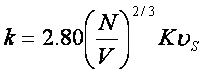
Here, N is Avogadro’s number, V is molar volume, K is
Boltzmann’s constant, and us is sonic velocity.
The Matlab program used to calculate thermal conductivity of liquids is klcalc.m.
It was also assumed that the thermal conductivity,
density, viscosity, and heat capacity of the solution is equal to that of the solvent B because the solution is so
dilute. In addition, the density of the
solvent is independent of temperature.
The Matlab program used to calculate liquid viscosity is liqmucalc.m.
Because of the unsatisfactory nature of the theory for
diffusion in liquids, it is necessary to rely on empirical expressions. The Wilke-Chang equation (BSL Eqn 17.4-8) is
used in this program and gives the diffusivity for small concentrations of
solute A in solvent B as
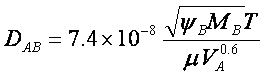
Here, VA is the molar volume of the solute
A at its normal boiling point, m is the viscosity of the
solution, yB is an “association parameter” for the solvent, MB
is the molecular weight of the solvent, and T is the absolute temperature.
Low Density Binary Gas Mixtures
Calculations involving low density gas mixtures
operate on several core assumptions.
First, low density implies ideal gases, and the ideal gas law was used
to calculate the density of the mixture.
In order to calculate the density of the mixture, an average molecular
weight of the mixture was determined by weighing the mole fractions of the
components with each pure component’s molecular weight. This was similarly performed for the heat
capacity, and an average heat capacity was associated with the gas mixture.
The thermal conductivity for gas mixtures at low
density may be estimated by BSL Eqn 9.3-17.
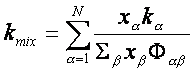
Here, xa are the mole
fractions, ka are the thermal conductivities of the pure chemical
species, and Fab is a dimensionless quantity that is a function of the
viscosities and molecular weights defined in BSL Eqn 1.4-16. The Matlab program used to calculate the
thermal conductivity of gas mixtures is mixkt.m.
The binary diffusivity of low density gas mixtures is
calculated using Chapman-Enskog kinetic theory.
Approximating concentration using the ideal gas law, the empirical
formula for diffusivity is expressed by BSL Eqn 17.3-12
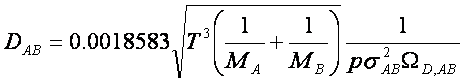
Here, T is temperature, M is the molecular weight of
the component, p is pressure, sAB is the characteristic diameter of the molecules
called the collision diameter, and WD,AB is a
dimensionless quantity called the collision integral and is a function of
dimensionless temperature. This value is
associated with Lennard-Jones parameters, given by Table E.2 in BSL. The Matlab program used to calculate the
diffusivity of gas mixtures is dcalc.m.